Four methods of pouring melted zirconia-corona bricks
Fused corundum bricks are made by melting aluminum oxide in an electric arc furnace and casting it into a model of a given shape.. After annealing and heat conservation, the required product is obtained by processing with diamond abrasive tools.
Introduction to Fused Zirconium Corundum Bricks

This product is divided into three types according to different crystal shapes and the amount of aluminum oxide. The first type is based on α-Al2O3 as the main crystalline phase, which is called α-corundum brick; the second type is based on α-Al2O3 and β-Al2O3 The main crystalline phase is mainly 1:1, and the α-phase content is slightly higher, what is called α, b- corundum brick; third type – it is mainly β-Al2O3 crystalline phase, which is called β-corundum brick.
Four ways to pour AZS bricks
When the fused zirconium corundum brick hardens, volume change, caused by a transition from liquid to solid, leads to the formation of shrinkage cavities of approximately 15-25%. As a result, there are various casting methods, which use hot water casting to minimize shrinkage cavities of fused zirconium-corundum bricks and take into account the erosive state of the part used, to concentrate shrinkage cavities at one end.
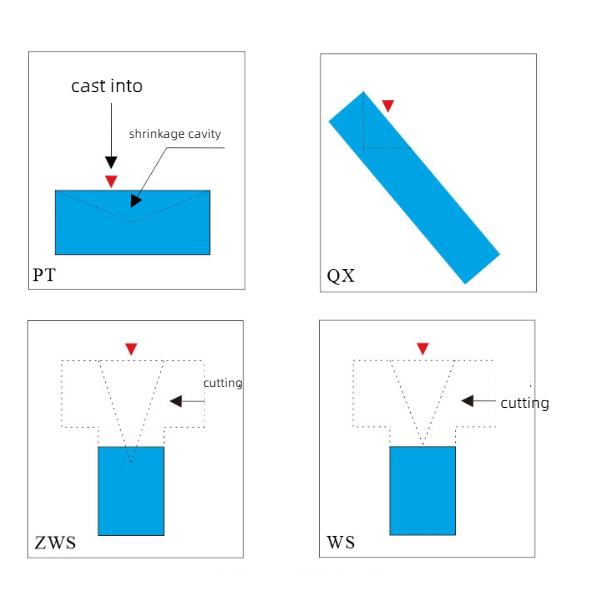
- Regular casting (PT) common casting method. The shrinkage cavity in the molten zirconium-corundum brick is located at the bottom of the casting hole. Used in such parts, as a top structure for glass furnaces, where corrosion occurs relatively slowly.
- For inclined casting (QX) inclined casting method is used, and shrinkage holes in fused zirconium-corundum alloy bricks are offset at the bottom (use bricks for dry pool walls). It is thanks to the inclined insulation method that the shrinkage holes are directed to the lower part when used.. Thus, shrink holes are concentrated at one end of the brick, while the other end is tight. Fused zirconium corundum bricks are usually used in those parts of the melting tank wall of glass furnace, which correspond to the erosion of the liquid level line in the glass.
- Casting without shrinkage (WS): After cooling and compacting the casting, part of the shrinkage cavity is removed from the fused zirconium-corundum brick without shrinkage cavity. Usually, using liquid holes in a dry glass kiln, pool walls and other details, causing severe corrosion.
- Casting without quasi-shrinkage (ZWS) – it's the same, same as ZWS, which is a fused zirconium-corundum brick with almost completely removed shrinkage cavities. Shrinkage cavities are also concentrated at the mouth of the casting. After the casting has cooled, most of the shrinkage cavities are cut out, leaving only a very small amount of shrinkage cavities on the cut surface. Commonly used as swimming pool wall bricks for glass melting furnaces.


 Rongsheng Refractories Group
Rongsheng Refractories Group